In the words of Amazon Chief Technology Officer Dr. Werner Vogels, “Without data, artificial intelligence is nothing.”
Speaking to a crowd of tech leaders at the United Nation’s AI for Good Summit in Geneva, Switzerland, Vogels talked about the evolution of artificial intelligence (AI) while stressing the pivotal role data plays in leveraging technology for the greater good.
“We’ve had AI tools for quite a number of years, and with generative AI, a whole new tool set is becoming available,” he said. “All of this is useless if we don't have access to data and the right data.”
As the world’s most comprehensive and broadly adopted cloud, Amazon Web Services (AWS) allows millions of customers to tap into their data at any time. But as Vogels explained at the summit, data is a privilege that not everyone has. So, in order to do good with data, we need to democratize access with open data initiatives, like the AWS Data Exchange, which allows for the acceleration of research and creation of new applications that positively impact society.
“With real-time data on historical patterns and current data, algorithms in AI can identify where we can proactively take action instead of doing things after the fact,” Vogels said.
For AWS customers dissecting data with AI and machine learning (ML) tools, action comes in many forms. Whether it’s climate change, health care, or transportation, businesses and organizations are already using these technologies to solve some of the world's most complex challenges.
During his talk, Vogels pointed to examples of AWS customers leveraging data to use AI and ML tools for good. Here’s a look at some of the businesses and organizations he says are actively working to change the world for the better.
Shrinking commercial cargo aviation to save lives
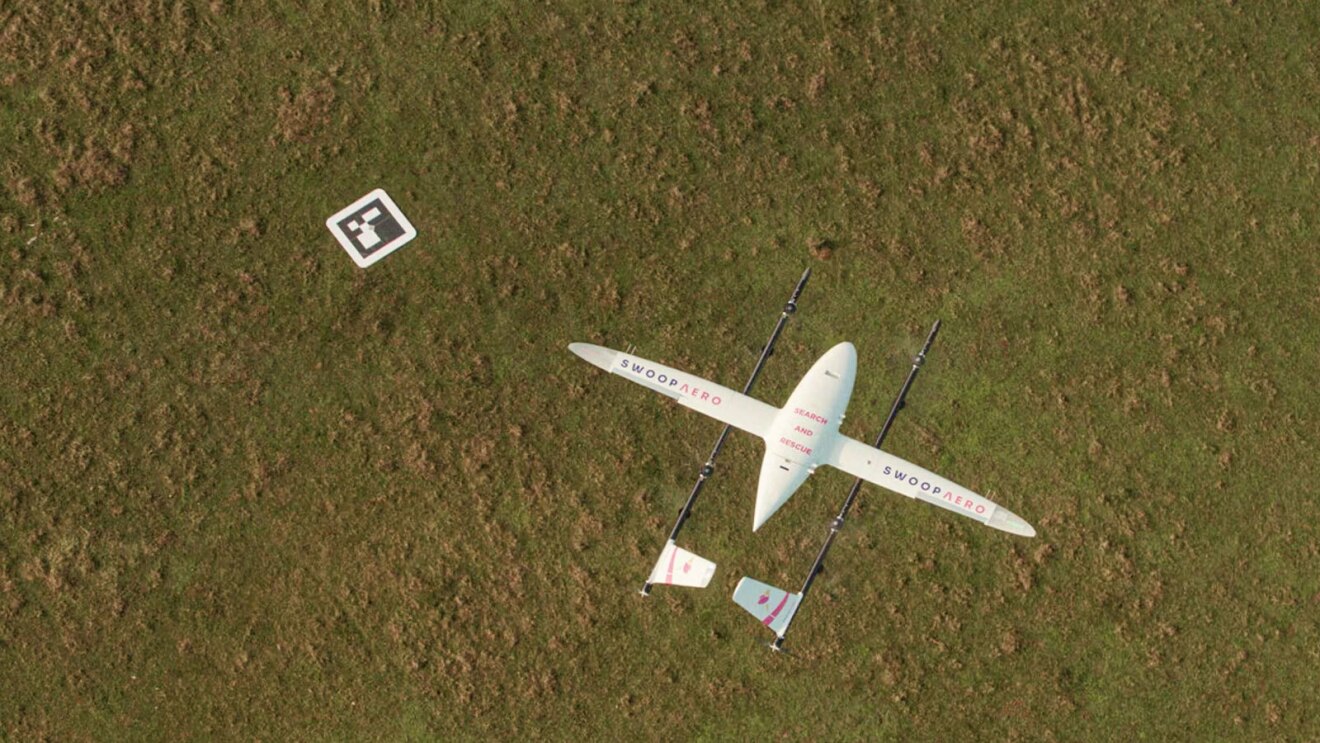

Swoop Aero uses AI to enable medical deliveries by using autonomous drones, particularly in remote and underserved areas. By running its platform on AWS, Swoop Aero can scale to support a single remote pilot controlling 30 or more aircraft throughout the world from its Remote Operations Center in Melbourne, Australia. Each pilot can fully fly aircraft across four continents beyond visual line of sight, maintaining continual situational awareness.
Swoop Aero uses AWS IoT to help its ML models do predictive maintenance, which involves monitoring and analyzing drone performance data to anticipate maintenance needs and address potential issues proactively. So far, Swoop Aero has supplied medicine to more than 3.5 million people around the world and has expanded its services to include mapping, search and rescue operations, and other deliveries.
Identifying patterns to protect children online

Safer can be used by any company to identify, remove, and report CSAM from content-hosting sites without a large investment in staff head count, unnecessary exposure of employees to disturbing material, or unforeseen legal risk. Thorn also collaborated with AWS to build software that uses Amazon Rekognition to help identify victims in sex trafficking investigations through the analysis of large datasets.
Synthesizing data to map the human brain
The Allen Institute uses AI and ML to advance brain research, including mapping brain circuits, analyzing neural activity, and modeling brain functions, leading to a deeper understanding of the brain and its disorders. High performance computing on AWS helps the Allen Institute store, access, and analyze data from the brain's approximately 200 billion cells.
Their Brain Science Platform provides access to high-quality data and web-based applications for researchers to explore the biological complexity of the mammalian brain. This platform is the largest open source database of brain cell data in the world, and it’s available through the AWS Public Dataset Program.
Sharing rice genes to reduce poverty and hunger
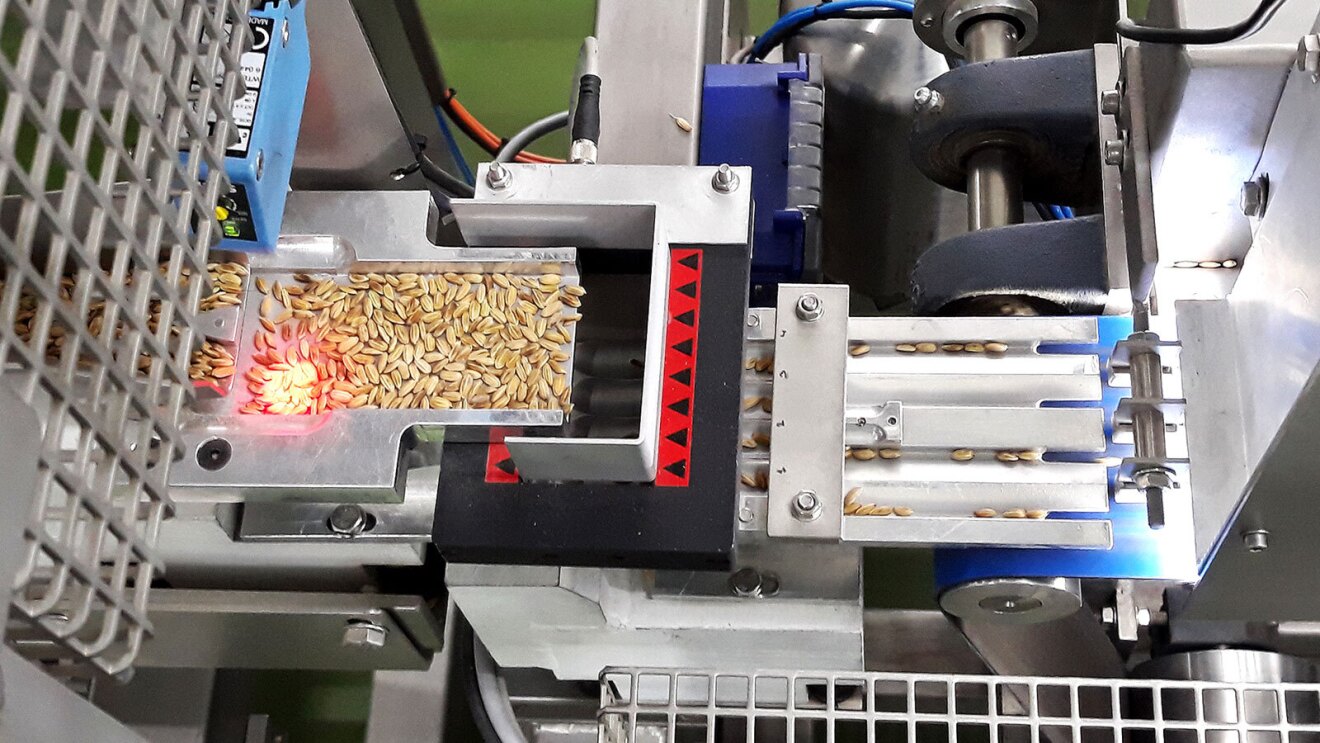

With the largest collection of rice genetic diversity in the world, the International Rice Research Institute (IRRI) uses AI and ML to reduce poverty and hunger among populations depending on rice-based agri-food systems. The IRRI Genebank contains 200,000 varieties of genes for safe keeping, sharing, and research. The organization’s advanced ML methods enable rapid understanding of genomic data and have led to the development of rice that is more tolerant to climate change. In addition to scientific research, the IRRI develops digital platforms that use AI algorithms to analyze and share agricultural data, fostering collaboration among researchers, farmers, and policymakers.
The AWS Cloud hosts the 3,000 Rice Genome Project, which is an international effort to sequence the genomes of 3,024 rice varieties from 89 countries. The open data provided by IRRI and other organizations contains more than 30 million genetic rice variations that anyone can use with AWS on-demand computing resources to perform analysis and create new products, without the cost of storing the data.
Casting cameras under water to improve fish farming
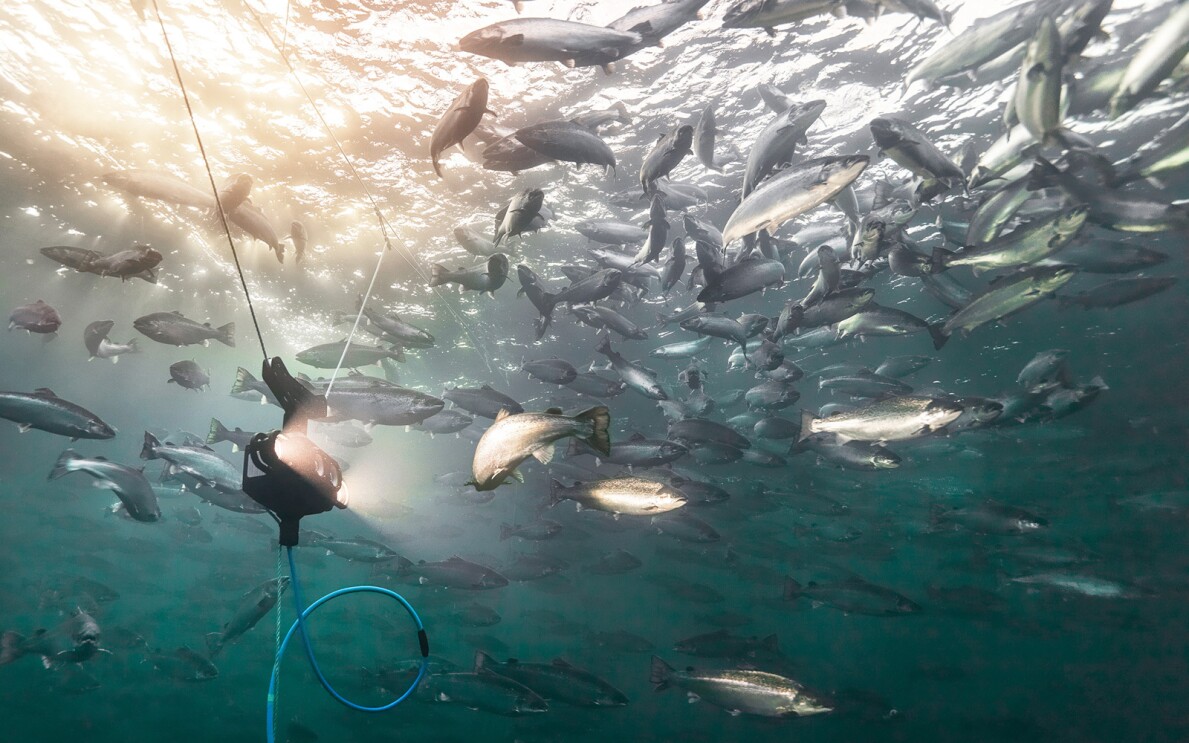

Aquabyte uses ML solutions and computer vision to monitor and optimize fish farming operations, enabling sustainable aquaculture practices and reducing environmental impact. The startup’s underwater 3D cameras capture images and videos of fish in aquaculture farms around the world. Machine learning algorithms, running on Amazon SageMaker, can estimate how much each fish weighs without removing it from the water. The system can also monitor the fish for sea lice and welfare, proving information for data-driven decision making. The analysis helps farmers stop the spread of diseases and reduce the cost of feed resulting in less waste and more efficiency.
In his series "Now Go Build," Vogels travels to Bergen, Norway, to meet with the founder of Aquabyte and see the use of underwater computer vision in action.
You can watch that video and more as Vogels explores startups around the globe that are using technology to innovative for good on Prime Video or YouTube.











